A great article on Ichiro Suzuki on MLB.com that is worth sharing
https://www.mlb.com/news/featured/ichiro-suzuki-lasting-impact-on-baseball-japan
Asian Baseball History and Culture is Our Passion

A great article on Ichiro Suzuki on MLB.com that is worth sharing
https://www.mlb.com/news/featured/ichiro-suzuki-lasting-impact-on-baseball-japan

The Los Angeles Dodgers have just released a fantastic video on Youtube called The Story of Nomomania. With great game footage and exclusive interviews with Hideo Nomo, Peter O’Malley, Mike Piazza, and Don Nomura, I think fans will truly enjoy watching.

On Thursday, July 10, 2025 SABR’s Asian Baseball Research Committee hosted its first Zoom event. Our guests were former Yakult Swallows closer and Texas Ranger Tony Barnette and author Aaron Fischman. Tony and Aaron spoke about their Casey- Award-nominated book, A Baseball Gaijin, as well as Tony’e experiences in Japanese baseball.
This fascinating event can now be view in its entirety on SABR’s YouTube channel.

by Robert K. Fitts
In 2022 Japanese baseball celebrated its official 150th birthday. Most officials and historians date the introduction of baseball to Japan to 1872 when American teacher Horace Wilson taught the game to his Japanese students. Recent research, however, has shown that the crew of the U.S.S. Colorado played against American residents of Yokohama in October 1871, and perhaps against Japanese residents of Osaka in January 1871[1] Now, a newspaper article shows that baseball was played as early as July 1869 in Kobe.
A few years ago, historian Aaron M. Cohen began sending me clippings about Japanese baseball from his files. Among the clippings was an article written by Harold S. Williams in 1976 discussing the origins of Japanese baseball. Williams was an Australian who lived in Kobe, Japan, from 1917 to his death in 1987, except for the war years. Williams wrote extensively about the early history of Kobe and Japanese culture.
In his article, “Shades of the Past: The Introduction of Baseball into Japan,” Williams argued “the names of those who actually first introduced the game into Japan is something which never will be known. Furthermore nobody knows, nobody can ever know, exactly where or precisely when the first game was played. Certainly it would have been a very modest and informal affair”[2] A sentence in the article caught my attention. He wrote: “in Kobe, on 4th August, 1869, about eighteen months after the port was opened, The Hiogo News reported: …one evening last week we saw as many as 7 or 8 men playing cricket and a still larger number playing baseball.”
Intrigued, I shared this with my colleague from Kawasaki, Japan, Yoichi Nagata. Yoichi went to the National Diet Library in Tokyo to track down the original source. The text of the article, appearing on page 434, is as follows.
“The exuberant spirit of youthful Kobe has been disporting itself for some days past a little out of the beaten track. This is a fact that, in spite of all kinds of adverse circumstances, the enthusiasm of a few cricketers has burst through the bonds that hitherto bound it, and bat, ball and stumps have been paraded through our streets. …The practice ground—no, it would not be right to call it by that name—the ball–splitting ground, or the ground upon which play has been carried on, has been the N.E. corner of the “sand patch” of a year ago—now well overgrown with weeds, grass, etc., etc. The best of this has been selected, the grass has been cut, and it makes a fair ground for practice. If anyone is skeptical on this point, he should join in an evening’s play, but novices should be fairly warned of the surrounding dangers, or the drains and stakes may cause a nasty tumble. The stakes are the corner posts of the different unsold lots, and those who have run against them say they are pretty firmly driven in. These are minor disadvantages, and the cricketeers say that a man never runs against them twice,—memory acts as a kindly warning, and one proof of their stability has hitherto been found quite sufficient.Truly, the “sand patch” has been used for purposes never dreamed of, and that it was apparently least fitted for. Two successful Race Meetings have been held on this non-elastic turf, and one evening last week we saw as many as 7 or 8 men playing cricket, and a still larger party playing baseball.We are pleased to hear it is the intention of the cricketeers to form a club, and wish them every success. Although there is sufficient talent here to form a good club, we fear the obstacles in the way of success are greater than are anticipated, unless the promoters are fortunate enough to secure a plot of ground at a very small expense, such, for instance, as an unused portion of a Race Course (should a Race Course be made here.) To buy or rent a piece of ground will entirely will be entirely beyond the means of such a club as can be formed here. A large piece of ground is required—say from 3,500 to 4,000 tsubos, and this at the lowest Japanese rental will amount to a very considerable figure yearly, to say nothing of the cost of preparing and keeping it in repair. The most feasible plan we have heard proposed is that permission should be obtained to use a certain portion of the N.E. corner of the Concession, level it, and cover it with mould, turf, &c. This scheme has few objections. The cost will be trifling, and in a few months, a decent practice grounds can be made. As the land is not likely to be required for some time, we think the Native Authorities would have very little objection to it being used for the purpose. We are aware the ground would be anything but perfect, and far from what a fine player would desire… .”
In March 2025 Yoichi and I returned to the Diet Library to search the Hiogo News for more early references to baseball. Unfortunately, we came up empty.
The “sand patch” mentioned in the Hiogo News article was not a particular location within Kobe but rather was a nickname for the entire area allocated for the foreign settlement. With a few exceptions, Japan was closed to foreigners from the beginning of the seventeenth century until American Admiral Matthew Perry entered Tokyo Bay with his Black Ships in 1853 and demanded access to the country for trade. The subsequent 1854 Convention of Kanagawa and 1858 Treaty of Amity and Commerce opened seven ports for trade and allowed for a foreign settlement, or Concession, at each port.
The Kobe Concession was opened on January 1, 1868. The land set aside for the foreign settlement was a barren sandy plain with poor drainage. Soon dubbed the “Sand Patch,” it became a swamp with knee deep quicksand during the rainy season and a dusty wasteland during the dry season. Early settlers began reclaiming the land and constructing trading houses and homes. By mid 1868, the area had been surveyed and laid out with staked plots ready for sale. Within the first year, the settlement’s small population (it contained about 200 Westerners in 1871) established two newspapers, social clubs, and on March 1, 1869, a horse racing club.

An 1870 plan of the Kobe Concession shows the location of the staked plots for sale and the approximate location of the ground used for cricket and baseball in July 1869. As the article clearly states that the ground was in the northeast corner of the concession and contained stakes marking the unsold lots, we can place the area just to the west of modern Kobe City Hall between Kyomachisuji Street on the west, Hanadokeisen Street on the north, Higashimachi-Suji Street on the east, and Kitamachi Street on the south.
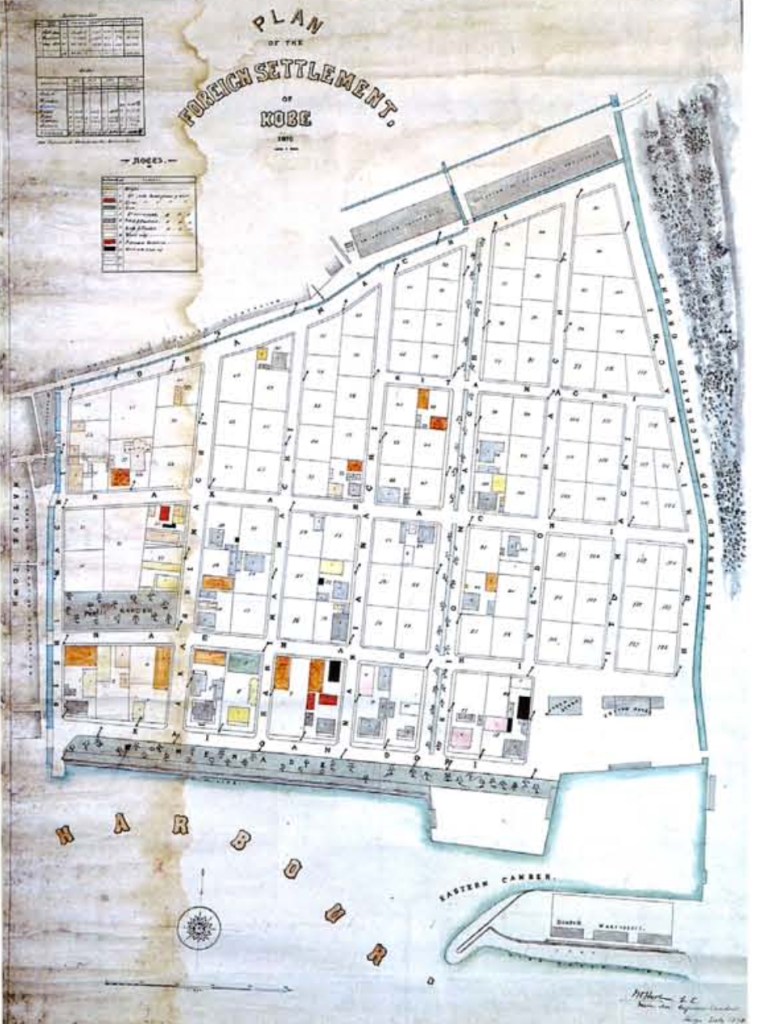
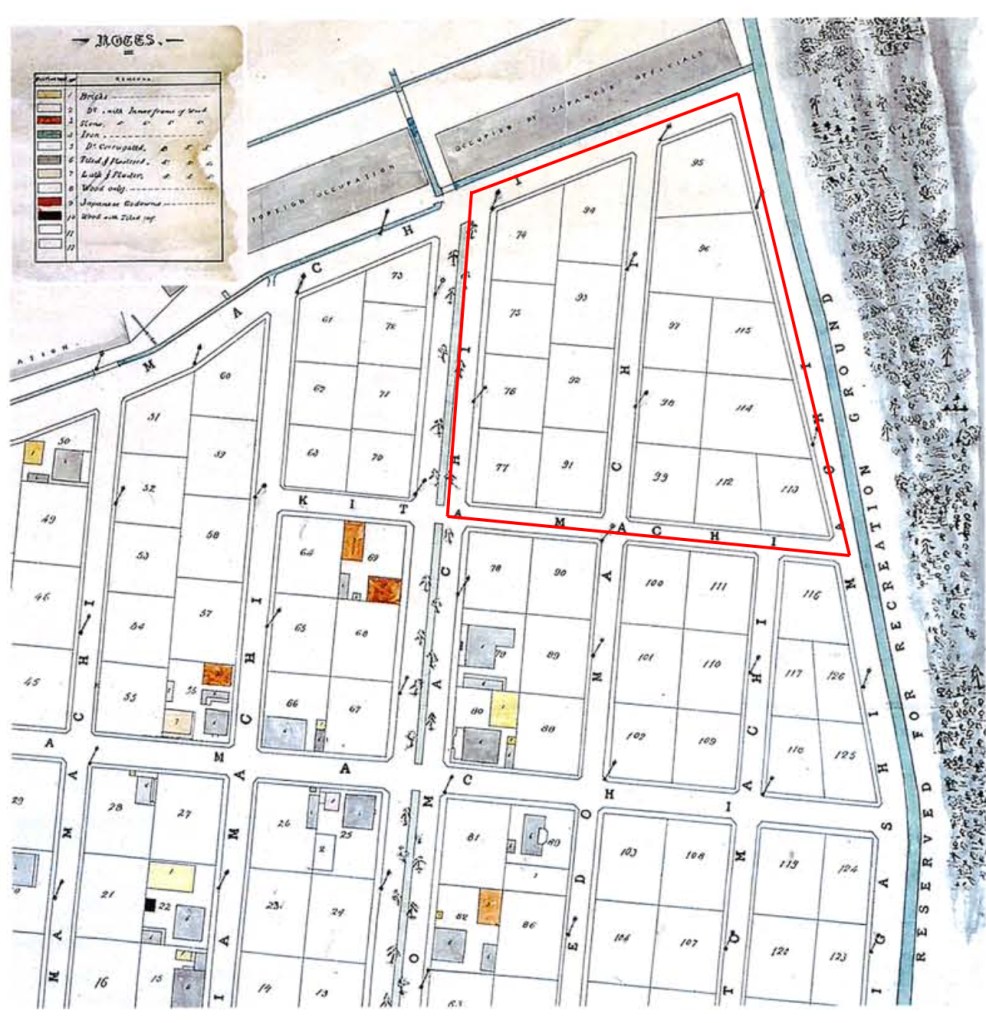

Sadly, Williams is correct that we may never know the identities of these early ballplayers. A complete list of early Kobe settlers that includes nationalities does not seem to exist. Therefore, we cannot identify the American residences who may have played in this July 1869 game.
In September 1870 the foreign residents of Kobe established the Kobe Regatta & Athletic Club and in 1872 reached an agreement with the Japanese authorities to create a recreation ground on the land just east of the concession where future cricket and baseball games were held.
With the digitization of newspapers and other sources from Meiji Japan, I expect that future researchers will find more evidence of early baseball in Japan. But Williams is probably correct that we will never know the exact date and location of first baseball game in Japan.
[1] Nobby Ito’s research on the 1871 game in Osaka is summarized in Michael Clair’s August 17, 2024, article on MLB.com “Search for Japan’s baseball origins unearths new possibility.”
[2] Williams’s article was originally published in the 1976 Journal of the American Chamber of Commerce in Japan and was republished in Culture, Power & Politics in Treaty Port Japan, 1854-1899: Key Papers, Press and Contemporary Writings, edited by J.E. Hoare (Amsterdam University Press, 2028).

by Yoichi Nagata
In the 2024 season, American baseball fans were curious to witness two Japanese players, Shohei Ohtani and Shota Imanaga, bowing to each other on the field during the warmup time before the regular season game between the Dodgers and the Cubs. Bows are seen everywhere on Japanese baseball grounds. Probably the most well-known ground bow is seen during the annual spring and summer Koshien high school tournaments. Players from each team line up on the both sides of home plate and bow facing each other before and after the game. It is a ritual in Japanese scholastic baseball.
When and where did the ritual of the pre-and post-game bow on the field begin? In 2022, the official 150th anniversary of Japanese baseball, the ad hoc baseball committee consisted of NPB, the Baseball Federation of Japan and the Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum concluded that the Tohoku Six-Prefecture Middle School Baseball Tournament in Sendai, Miyagi, sponsored by the Second Higher School, initiated the ritual on November 3-5, 1911. It was incorporated into a regulation of Koshien baseball in 1915, when the tournament was first held.
The history book of Zenkoku Chuto Gakko Yakyu Taikaishi (History of National Middle-School Baseball Tournament) published in 1929 reveals the idea behind the ritual.
“Bushido (the spirit of Samurai) and sportsmanship have elements in common. However, Yakyu is baseball based on Bushido, apart from American professional baseball. And this is a baseball tournament to promote and spread baseball in Japan. Scholastic baseball must follow the ritual of the Japanese way, “The Bushido match starts with a bow and ends with a bow.”
However, I have found Tokyo newspaper Yomiuri Shimbun of April 9, 1897 reporting the ritual in the game between Yamaguchi Higher School and Kumamoto Daigo Higher School in Fukuoka, Kyushu. “Players of the two teams came out to the field, and formed two lines and bowed to each other.”
Besides Yomiuri, two Fukuoka local papers of April 6, 1897, Fukuryo Shimbun and Fukuoka Nichinichireported alike.
The Yamaguchi school, hungry for a good opponent, sent a letter of challenge to the Kumamoto school for a baseball game. In front of the eyes of professors and students from both schools, the Kumamoto school pounded the Yamaguchi school, 21 to 2.
“The moment the game was over yells erupted from both cheering groups, “Banzai Daigo Higher School!” and “Banzai Yamaguchi Higher School!” Amidst of the shouts, the nine players of each team made its own line and bowed facing each other in the same manner of the pregame way (Fukuryo Shimbun and Fukuoka Nichinichi Shimbun of April 4, 1897).”
The ritual of the pre-and post-game bow, we now see in high school games at Koshien and college games at Jingu Stadium, was performed fourteen years before the Sendai tournament. However, considering the fact that baseball was introduced to the land of Bushido around 1870, it is unthinkable that for almost 30 years prior to the Fukuoka game, bows had not been performed on baseball grounds.

I am also interested in another example of “first” in Japanese baseball history. The first admission-charged game was considered for a long time Game 1 between the St. Louis College alumni team from Honolulu and Keio University at Tsunamachi ground, Tokyo, on October 31, 1907 to pay off the travelling expenses of the Hawaii team. However, I have found four newspapers, Tokyo Mainichi Shimbun, Jiji Shimpo, Kokumin Shimbun, and Japan Weekly Mail, reporting that the game between Yokohama Cricket and Athletic Club (YC&AC: a sports club of foreign residents) and Waseda University at Yokohama Park on October 12, 1907, nineteen days before the St. Louis and Keio game, was a paid game to keep the spectators section in order. After my continuous research since then, I am not able to conclude that this was the first admission-charged game yet, because a newspaper suggests some games were so before the YC&AC and Waseda game. The paper doesn’t specify which games were.
Recently, we learned that baseball was played in Japan as early as 1869, however, it was thought for many years baseball arrived in Japan in the early 1870s. I wonder how far back firsts of the ritual of pre-and post game bow and admission charged game stretch.

In October 2003, I had the pleasure of interviewing former Carp manager Takeshi Koba before an oldtimers’ game at Tokyo Dome. Koba played for the Carp from 1958 to 1969 but is more famous for managing Hiroshima during their famous Akaheru (Red Helmet) era. From 1975 to 1985 Koba led the Carp to ten winning seasons and three Japan Series championships. He was elected to the Japan hall of fame in 1999.
How does one become a manger in Japanese baseball? You ask the owner. There are many younger managers nowadays who have no coaching experience and of course no managing experience and yet they are able to become managers. I think that it’s different from the system in the United States. In Japan if you play and you become famous then you can become a manager.
In my first year as a manager, I was able to win the league championship. But you never know how many years you can actually be a manager. If you don’t get results, the fans aren’t happy, and the team nudges you to quit. So, what do you do? You have to play ball, you have to make sure that people who come to watch enjoy themselves, and also you have to win. So, you have to make sure that the players get together as one and work towards winning. My job as the manager was to make sure that the team was together on that. And when you eventually get fired, my goal was to not have regrets.
When you take over a team and you have no good pitchers and the defense is bad and you really have to start from scratch then it takes quite a long time to build a winning team, but usually there are only certain sections or certain players who need improvement. It was my job as a manager to reach out to those players and together with the coaches to nurture them in certain directions or in certain ways. Every year I would have to figure out who those players were and pick them out. There are only nine positions in baseball and not including the pitcher, eight positions. I always said that I wanted six or seven position players to be there until the end of the game.
When I became the manager, we had on our team Koji Yamamoto and Sachio Kinugasa. These were special players. They were recognized by all of the other ballplayers as stars, and they were why we were able to win the 1975 championship. They became role models for the younger players throughout the year. All I needed to say to the young players was, “If you want to catch up to Yamamoto and Kinugasa, if you want to exceed these two, you have to practice harder.” That’s all that was required.
I was also really very lucky with my two foreign players. Gail Hopkins and Richie Scheinblum could hit and play defense. They were all-round players. I could count on them from the beginning of the game to the end of the game. So, it made managing very easy. When U.S. players come to Japan, there are coming here after really working very hard in the American Minor and Major Leagues. As a manager I asked Jim Lefebvre to scout some players for us. I asked him for players who could adjust to the style here in Japan. Lefebvre said that it really depended on the wife. If the wife can be interested in coming to Japan, if the wife agrees and enjoys the experience then that’s very important. So, I asked for such players.
When I was a manager, I think that I did everything I wanted to do and I put my whole self into it. I gave it my best. There are many people who say that I am a Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde—that I have a dual personality because outside of the field I’m very quiet and I don’t say much and don’t complain but once I’m on the field my eyes change, and I become very severe. There are some players who say that I hit them! I never hit anybody, but I put my all into it, and I made sure that the players understood that I’m putting my all into it because that’s an important part of creating a winning team.
I always told my players from the very beginning of the season that if they had complaints or there was something about the team or the way I was managing that they didn’t like that they could talk to me at any time. And if I could, I would solve that problem to the best of my abilities. Throughout the season, I thought if I could do that it would be best. I didn’t want to be at the end of the season with a player not doing his best and not performing well for the team. I wanted to avoid that kind of situation as it made everyone dissatisfied.
As a manager, I talked with my coaches, I talked with my staff, and I told them throughout the year that I was confident that I would do my best for the team but if during practice you find something that we need to do more or if another team was doing something that was better then tell me about it. I was proud of what I was doing but I might not have been doing it the best way so if there was something else that’s better, I wanted them to tell me about it. One thing that I think I succeeded in doing well was to create good switch hitters. For example, there were pitchers who the scouts brought to the team but we decided that they weren’t very good as pitchers so we decided to use them as outfielders. If they had the necessary legs and powerful bodies, I would tell them, “Why don’t you work hard and try to become a switch hitter?” Many of my athletes succeed in becoming very good switch hitters. With a group of good switch hitters we were able to create a good team. I think that is why we were able to compete for the league championship for many years.
When I was playing with a company team, one day I had injured my right finger and I came to the field in street clothes, carrying my right arm, obviously in pain. My manger was very angry with me. He said, “Go back in and put your uniform on!” After I put my uniform on again, he told me to stand in the batter’s box and he threw balls right at me. I was scared so I put my bat in front of me with my left hand because my right was injured. Somehow the ball was hitting the bat that I held with my left hand and my manger yelled, “See you can do it! If you work for one week, you can develop your left arm so you can hit with your left arm.” As you can see, my body is not very big. He said, “If you take time off, your body is going to be less developed so you can’t take any time off. You have to always be in there and keep playing.” That was an important lesson.

[Editor’s note: In 1963, Koba’s sixth year of professional ball, Koba was in contention for the Central League batting title when he was hit in the face with a pitch and hospitalized.]
The injury definitely influence how I played afterwards, maybe it was just a matter of several millimeters but I was no longer able to hit the ball on the meat of the bat so my contact became weaker and therefore I didn’t have as many hits. My average went from .339 to .219 the next year. So, I asked myself how else can I contribute to the game? And I thought, I can use my legs. So, I started stealing bases and I led the league in stolen bases the following year. That’s what I told my athletes, “Ask yourself, how you can contribute to the game.”
When I was a manager, I always went to see the instructional league in Florida and we sent our young players there to participate. After the regular season here, I would go over and watch these young American players train and they would be working very hard. Most of them were from A or AA and were hoping to make it up to the AAA or Major League level. I took my young players with me because I wanted them to see what kind of severe reality, what kinds of conditions, the U.S. Minor Leaguers were playing in. U.S. players were given only $12 or $13 per day to participate in this. And if they didn’t perform well, they were put back down into the lower-level teams. I wanted the Carp players to understand this. I think that because the Carp players were actually able to see it for themselves, they were stimulated to improve more.
I was the manager of both Hiroshima and Yokohama. I was the manager of Hiroshima for eleven years. Managers of the other teams would say, “Hey, why are you practicing so hard?” Even when we were on the road before away games, I would always make sure that there were opportunities to practice just as hard. I think that the major difference between American and Japanese baseball, is that in America there is a Rookie League, A, AA, AAA, a whole system where the athletes who come up from the bottom can improve and move up to the next level. But in Japan, there is only the major club and the farm team. So, there are always about ten people, or more, in the farm who don’t quite have the bodies yet, don’t have the techniques yet to play in the major league. If you are always playing in the games you can gain the experience you need but if you aren’t in the games, you have to practice that much harder so that when it’s your turn to play in the games you can play well. If you don’t practice very hard, you can not surpass the other players and get into the major league. The other teams said, “Oh you practice so hard, you must always be tired.” But the tradition of hard practices still continues on the Hiroshima team today. I think because we had such hard practices the younger athletes grew and developed and matured.